LeNet¶
ConvNet Image Classification
- class lucid.models.LeNet(conv_layers: list[dict], clf_layers: list[int], clf_in_features: int, _base_activation: ~typing.Type[~lucid.nn.module.Module] = <class 'lucid.nn.modules.activation.Tanh'>)¶
Overview¶
The LeNet base class provides a flexible implementation for defining various versions of the LeNet architecture, including LeNet-1, LeNet-4, and LeNet-5.
It allows the configuration of convolutional and fully connected layers through arguments, making it adaptable for different use cases.
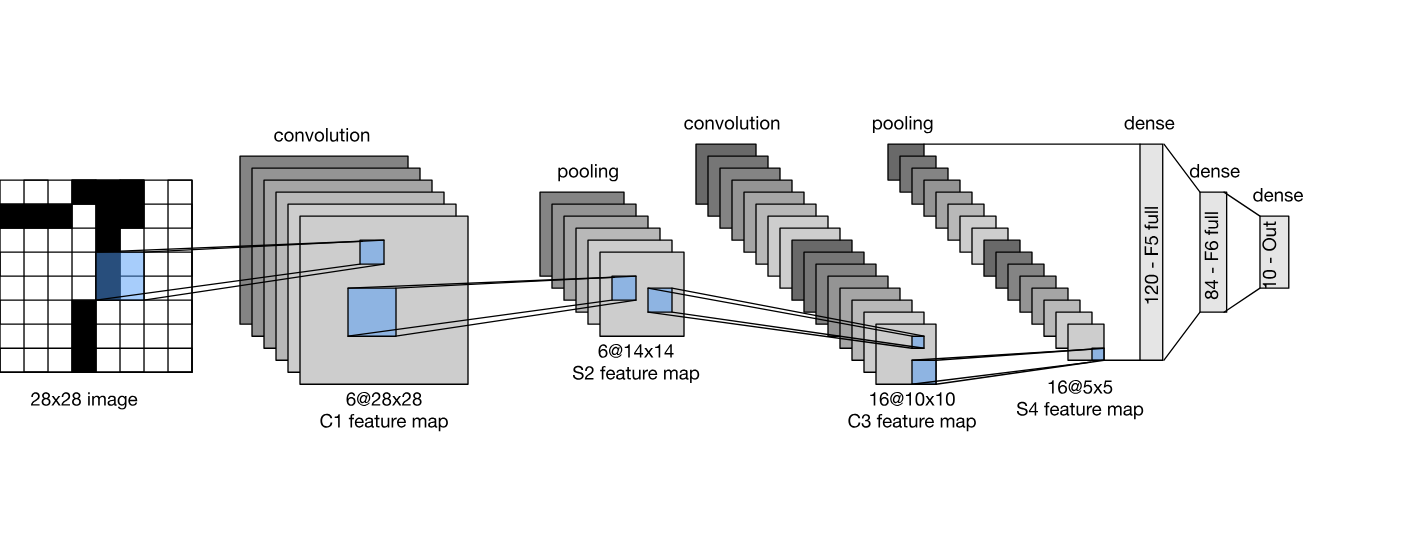
Class Signature¶
class LeNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
conv_layers: list[dict],
clf_layers: list[int],
clf_in_features: int,
) -> None
Parameters¶
conv_layers (list[dict]) A list of dictionaries specifying the configuration of the convolutional layers. Each dictionary should define the number of output channels (out_channels) and optionally other parameters such as kernel size, stride, and padding.
clf_layers (list[int]) A list specifying the sizes of fully connected (classifier) layers. Each entry represents the number of units in the respective layer.
clf_in_features (int) The number of input features for the first fully connected layer. This is determined by the output size of the feature extractor.
Attributes¶
feature_extractor (nn.Sequential) A sequential model containing the convolutional and pooling layers.
classifier (nn.Sequential) A sequential model containing the fully connected layers.
Methods¶
forward(x: Tensor) -> Tensor Performs the forward pass through the feature extractor and classifier.
def forward(self, x): x = self.feature_extractor(x) x = x.view(x.shape[0], -1) # Flatten x = self.classifier(x) return x
Example Usage¶
Below is an example of defining and using a LeNet-based architecture:
import lucid.models as models
# Define a custom LeNet architecture
custom_lenet = models.LeNet(
conv_layers=[
{"out_channels": 6},
{"out_channels": 16},
],
clf_layers=[120, 84, 10],
clf_in_features=16 * 5 * 5,
)
# Sample input tensor (e.g., 32x32 grayscale image)
input_tensor = lucid.Tensor([...])
# Forward pass
output = custom_lenet(input_tensor)
print(output)