R-CNN¶
ConvNet Two-Stage Detector Object Detection
- class lucid.models.RCNN(backbone: Module, feat_dim: int, num_classes: int, *, image_means: tuple[float, float, float] = (0.485, 0.456, 0.406), pixel_scale: float = 1.0, warper_output_size: tuple[int, int] = (224, 224), nms_iou_thresh: float = 0.3, score_thresh: float = 0.0, add_one: bool = True)¶
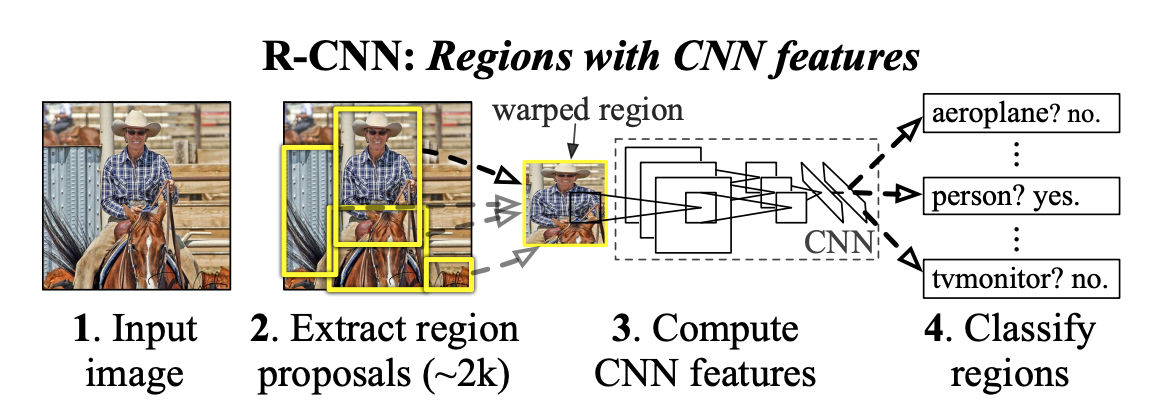
The RCNN implements the classic Region-based Convolutional Neural Network architecture for object detection. It integrates region proposal extraction, feature warping, CNN feature extraction, and classification, following the original R-CNN pipeline introduced by Ross Girshick et al.
Class Signature¶
class RCNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(
backbone: nn.Module,
feat_dim: int,
num_classes: int,
*,
image_means: tuple[float, float, float] = (0.485, 0.456, 0.406),
pixel_scale: float = 1.0,
warper_output_size: tuple[int, int] = (224, 224),
nms_iou_thresh: float = 0.3,
score_thresh: float = 0.0,
add_one: bool = True,
)
Parameters¶
backbone (nn.Module): A convolutional feature extractor shared across all region proposals.
feat_dim (int): Dimensionality of the backbone’s feature output.
num_classes (int): Number of object classes to classify (excluding background unless add_one=True).
image_means (tuple[float, float, float], optional): Per-channel RGB means for input image normalization. Default is ImageNet mean.
pixel_scale (float, optional): Pixel value scaling factor applied to input images. Default is 1.0.
warper_output_size (tuple[int, int], optional): The fixed resolution to which proposed regions are resized (e.g., 224x224).
nms_iou_thresh (float, optional): IoU threshold for Non-Maximum Suppression during prediction. Default is 0.3.
score_thresh (float, optional): Classification score threshold below which detections are discarded.
add_one (bool, optional): If True, adds background class at index 0, shifting all class indices.
Architecture¶
The R-CNN architecture consists of the following components:
Region Proposal (Selective Search):
Uses category-independent heuristics to propose candidate bounding boxes.
Selective Search merges superpixels based on texture, color, size, and fill similarity.
Produces ~2k regions per image.
Feature Extraction:
Each proposed region is warped (cropped and resized) to warper_output_size.
These warped patches are passed through the shared backbone CNN.
Features are then pooled and flattened for classification.
Classification and Localization:
Each region is classified using a fully-connected head.
Optionally, bounding box regression can be applied for precise localization.
Inference and NMS:
Predictions below score_thresh are filtered out.
For each class, Non-Maximum Suppression is applied using nms_iou_thresh to remove redundant overlapping detections.
Examples¶
Basic Usage
import lucid.nn as nn
import lucid.random
import lucid
# Define a simple convolutional backbone
class ToyBackbone(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.net(x)
return x.flatten(1) # (N, C)
# Instantiate backbone and RCNN
backbone = ToyBackbone()
model = nn.RCNN(backbone, feat_dim=64, num_classes=3)
# Dummy input tensor
input_ = lucid.random.randn(1, 3, 600, 800)
# Predict
output = model.predict(input_)
print(output["boxes"].shape, output["scores"].shape, output["labels"].shape)
Explanation
The image is first processed to generate region proposals using Selective Search. Each proposed region is resized and passed through the shared CNN (backbone), followed by a classification head that predicts object categories. Non-Maximum Suppression removes redundant overlapping boxes, and final predictions are returned.
Custom Configuration
class SmallBackbone(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.conv(x).flatten(1)
# Smaller model with adjusted feature dimension
backbone = SmallBackbone()
model = nn.RCNN(
backbone=backbone,
feat_dim=32,
num_classes=2,
warper_output_size=(112, 112),
nms_iou_thresh=0.5,
score_thresh=0.1,
add_one=False
)
input_ = lucid.random.randn(1, 3, 512, 512)
output = model.predict(input_)
print(output["boxes"].shape, output["scores"].shape, output["labels"].shape)