lr_scheduler.StepLR¶
- class lucid.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer: Optimizer, step_size: int, gamma: float = 0.1, last_epoch: int = -1, verbose: bool = False)¶
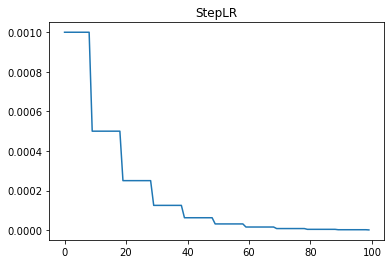
The StepLR learning rate scheduler reduces the learning rate by a fixed factor (gamma) every step_size epochs. This is useful for training scenarios where learning rate adjustments at regular intervals help in better convergence.
Class Signature¶
class StepLR(
optimizer: Optimizer,
step_size: int,
gamma: float = 0.1,
last_epoch: int = -1,
verbose: bool = False
)
Parameters¶
optimizer (Optimizer): The optimizer whose learning rate needs to be scheduled.
step_size (int): Number of epochs between learning rate reductions.
gamma (float, optional): The factor by which the learning rate is multiplied every step_size epochs. Default: 0.1.
last_epoch (int, optional): The index of the last epoch when resuming training. Default: -1.
verbose (bool, optional): If True, logs learning rate updates at each step. Default: False.
Mathematical Formula¶
The learning rate at epoch \(t\) is computed as:
Where: - \(\eta_t\) is the learning rate at epoch \(t\). - \(\eta_0\) is the initial learning rate. - \(\gamma\) is the decay factor. - \(\lfloor \cdot \rfloor\) represents the floor function.
Methods¶
get_lr() -> list[float]: Computes the updated learning rate(s) based on step decay.
step(epoch: Optional[int] = None) -> None: Updates the learning rate based on the current epoch.
Usage Example¶
import lucid.optim as optim
from lucid.optim.lr_scheduler import StepLR
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
scheduler = StepLR(optimizer, step_size=5, gamma=0.5)
for epoch in range(20):
optimizer.step()
scheduler.step()
print(f"Epoch {epoch+1}, Learning Rate: {scheduler.last_lr}")
Note
StepLR is useful when a constant learning rate decay at fixed intervals is preferred over continuous decay.