lr_scheduler.CyclicLR¶
- class lucid.optim.lr_scheduler.CyclicLR(optimizer: Optimizer, base_lr: float, max_lr: float, step_size_up: int, step_size_down: int | None = None, mode: Literal['triangular', 'triangular2', 'exp_range'] = 'triangular', gamma: float = 1.0, scale_fn: Callable[[int], float] | None = None, cycle_momentum: bool = True, last_epoch: int = -1, verbose: bool = False)¶
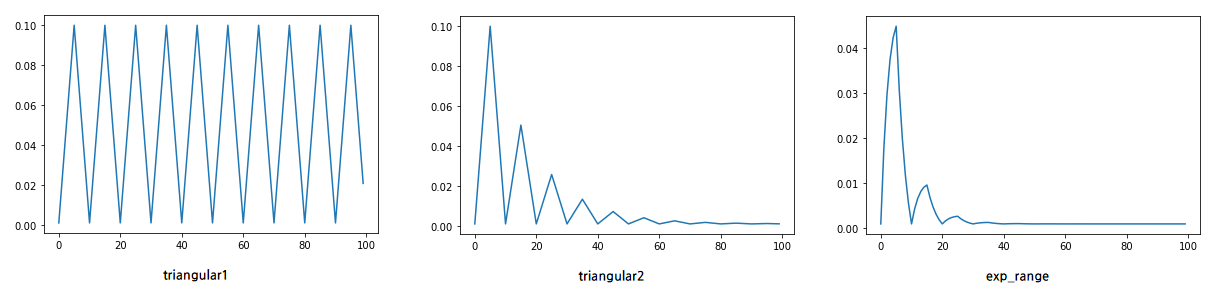
The CyclicLR learning rate scheduler varies the learning rate cyclically between a minimum (base_lr) and a maximum (max_lr) over a specified number of steps. This helps in escaping sharp local minima and improving convergence.
Class Signature¶
class CyclicLR(
optimizer: Optimizer,
base_lr: float,
max_lr: float,
step_size_up: int,
step_size_down: int | None = None,
mode: Literal["triangular", "triangular2", "exp_range"] = "triangular",
gamma: float = 1.0,
scale_fn: Callable[[int], float] | None = None,
cycle_momentum: bool = True,
last_epoch: int = -1,
verbose: bool = False,
)
Parameters¶
optimizer (Optimizer): The optimizer whose learning rate needs to be scheduled.
base_lr (float): Lower bound of the learning rate cycle.
max_lr (float): Upper bound of the learning rate cycle.
step_size_up (int): Number of iterations in the increasing half of the cycle.
step_size_down (int, optional): Number of iterations in the decreasing half of the cycle. Defaults to step_size_up.
mode (str, optional): Defines the shape of the cycle. Options are “triangular”, “triangular2”, and “exp_range”. Default: “triangular”.
gamma (float, optional): Scaling factor for “exp_range” mode. Default: 1.0.
scale_fn (Callable[[int], float], optional): Custom function for scaling LR per cycle.
cycle_momentum (bool, optional): If True, momentum is cycled inversely with the learning rate. Default: True.
last_epoch (int, optional): The index of the last epoch when resuming training. Default: -1.
verbose (bool, optional): If True, logs learning rate updates at each step. Default: False.
Mathematical Formula¶
The learning rate at step \(t\) follows the formula:
Where: - \(\eta_t\) is the learning rate at step \(t\). - \(\eta_{\min}\) and \(\eta_{\max}\) are base_lr and max_lr respectively. - \(c\) is the cycle index. - \(s(c)\) is the scaling factor, determined by the selected mode.
Methods¶
get_lr() -> list[float]: Computes the updated learning rate(s) for the current step.
step(epoch: Optional[int] = None) -> None: Updates the learning rate based on the current iteration.
Usage Example¶
import lucid.optim as optim
from lucid.optim.lr_scheduler import CyclicLR
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
scheduler = CyclicLR(optimizer, base_lr=0.001, max_lr=0.006, step_size_up=5, mode='triangular')
for epoch in range(30):
optimizer.step()
scheduler.step()
print(f"Epoch {epoch+1}, Learning Rate: {scheduler.last_lr}")
Note
CyclicLR is effective for scenarios where fluctuating the learning rate helps avoid sharp local minima and accelerates convergence.