VGGNet¶
ConvNet Image Classification
- class lucid.models.VGGNet(conv_config: list[int | str], num_classes: int = 1000)¶
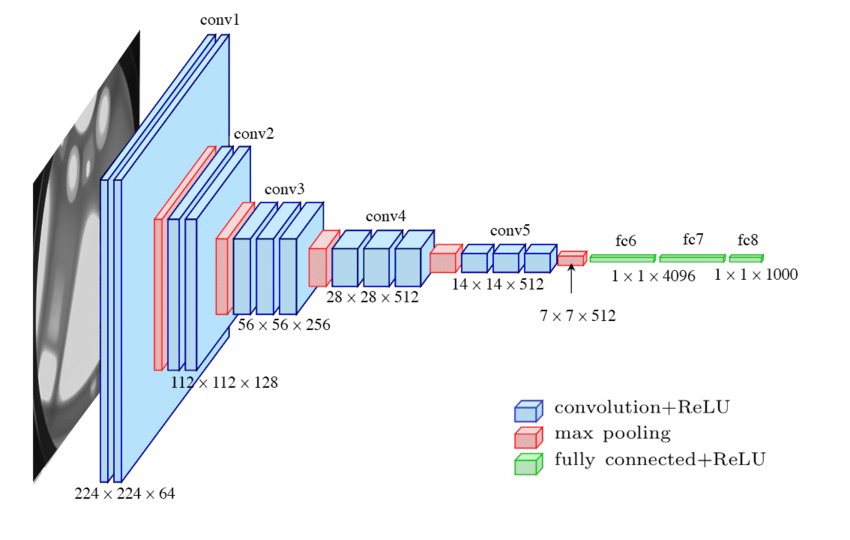
The VGGNet module in lucid.nn serves as a base class for creating VGG network variants (e.g., VGG-11, VGG-13, VGG-16, VGG-19). It provides a flexible architecture defined by a configurable list of convolutional and pooling layers.
Class Signature¶
class VGGNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config: List[Union[int, str]], num_classes: int = 1000)
Parameters¶
config (List[Union[int, str]]): A list defining the architecture of the network. Each integer specifies the number of channels in a convolutional layer, and ‘M’ indicates a max-pooling layer.
num_classes (int, optional): The number of output classes for the classifier. Default is 1000.
Attributes¶
features (nn.Sequential): A sequential container of convolutional and pooling layers as defined by the configuration.
avgpool (nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d): Adaptive average pooling layer that reduces spatial dimensions to (7, 7).
classifier (nn.Sequential): The fully connected layers for classification, including dropout and ReLU activations.
Methods¶
_make_layers(config: List[Union[int, str]]) -> nn.Sequential: Converts the configuration list into a sequential container of layers.
forward(x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor: Performs the forward pass of the network.
Examples¶
Defining a Custom VGG Configuration
import lucid.nn as nn
# Custom configuration
custom_config = [64, 'M', 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M']
# Create a VGGNet with the custom configuration
model = nn.VGGNet(config=custom_config, num_classes=10)
input_tensor = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
output = model(input_tensor)
print(output.shape) # Shape: (1, 10)
Explanation
The custom_config specifies two convolutional layers with 64 and 128 channels, respectively, followed by max-pooling layers, and two consecutive convolutional layers with 256 channels.