YOLO-v1¶
ConvNet One-Stage Detector Object Detection
- class lucid.models.YOLO_V1(in_channels: int, split_size: int, num_boxes: int, num_classes: int, lambda_coord: float = 5.0, lambda_noobj: float = 0.5)¶
The YOLO_V1 class implements the original YOLO (You Only Look Once) model for real-time object detection, as proposed by Redmon et al. (2016).
It divides the input image into an \(S \times S\) grid and predicts bounding boxes, objectness scores, and class probabilities for each cell.
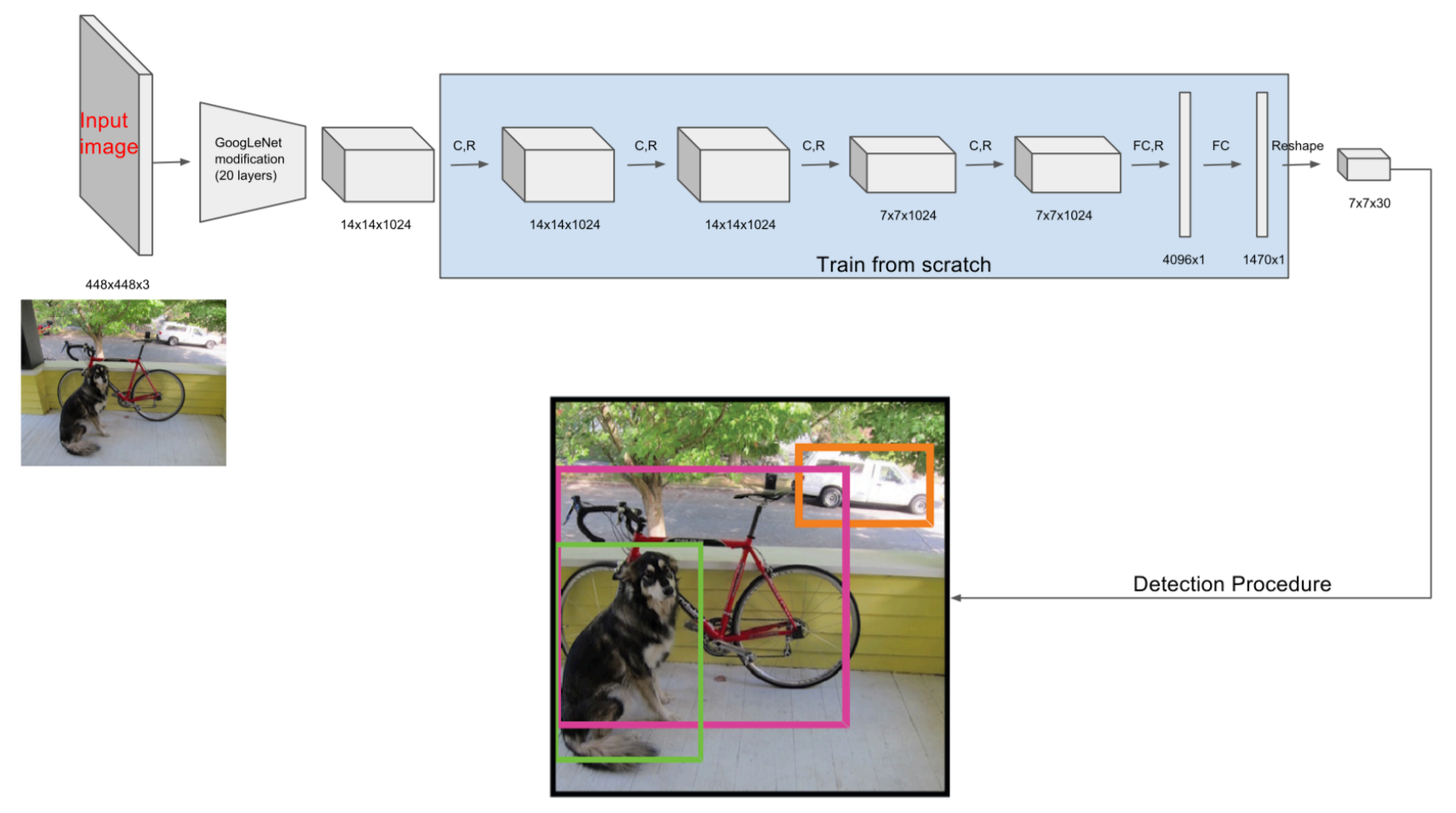
Class Signature¶
class YOLO_V1(
in_channels: int,
split_size: int,
num_boxes: int,
num_classes: int,
lambda_coord: float = 5.0,
lambda_noobj: float = 0.5,
)
Parameters¶
in_channels (int): Number of input image channels, typically 3 for RGB.
split_size (int): Number of grid divisions per side (S), meaning the input is divided into \(S \times S\) cells.
num_boxes (int): Number of bounding boxes (B) predicted per grid cell.
num_classes (int): Number of object classes to predict (C).
lambda_coord (float): Weight for the coordinate loss (default: 5.0).
lambda_noobj (float): Weight for the no-object confidence loss (default: 0.5).
Input Format¶
The target tensor from the dataset should have shape:
(N, S, S, 5 * B + C)
Where: - S is split_size (grid size), - B is num_boxes (bounding boxes per cell), - C is num_classes.
Each vector at (i, j) of shape (5 * B + C) contains: - For each box (B): (x, y, w, h, conf) - For the cell: one-hot class vector of length C
Returns¶
Use the forward method for predictions:
preds = model(x)
preds (Tensor): Tensor of shape (N, S, S, B * 5 + C) containing all bounding box and classification predictions.
Loss is computed using:
loss = model.get_loss(x, target)
loss (Tensor): Scalar total loss for object detection, including coordinate, confidence, and classification losses.
Loss Formula¶
The total YOLO loss is defined as:
Where: - \(\mathbb{1}_{ij}^{\text{obj}}\) indicates that object exists in cell i for box j, - \(\hat{C}_i\) is the predicted confidence, - \((x_i, y_i, w_i, h_i)\) are bounding box values, - \(p_i(c)\) is the class probability.
Methods¶
Examples¶
import lucid
import lucid.nn as nn
from lucid.models.objdet import YOLO_V1
model = YOLO_V1(
in_channels=3,
split_size=7,
num_boxes=2,
num_classes=20
)
# Forward pass
x = lucid.rand(16, 3, 448, 448)
preds = model(x)
# Compute loss
target = lucid.rand(16, 7, 7, 5 * 2 + 20)
loss = model.get_loss(x, target)
loss.backward()
Tip
YOLO expects bounding boxes as relative coordinates: - x, y are center positions relative to the grid cell. - w, h are normalized by image width and height.
Warning
The most confident bounding box (highest IoU with ground truth) is chosen for loss computation. Make sure your dataset follows the expected shape: (N, S, S, 5 * B + C).