EfficientFormer¶
Transformer Vision Transformer Image Classification
- class lucid.models.EfficientFormer(depths: list[int], embed_dims: int | None = None, in_channels: int = 3, num_classes: int = 1000, global_pool: bool = True, downsamples: list[bool] | None = None, num_vit: int = 0, mlp_ratios: float = 4.0, pool_size: int = 3, layer_scale_init_value: float = 1e-05, act_layer: type[~lucid.nn.module.Module] = <class 'lucid.nn.modules.activation.GELU'>, norm_layer: type[~lucid.nn.module.Module] = <class 'lucid.nn.modules.norm.BatchNorm2d'>, norm_layer_cl: type[~lucid.nn.module.Module] = <class 'lucid.nn.modules.norm.LayerNorm'>, drop_rate: float = 0.0, proj_drop_rate: float = 0.0, drop_path_rate: float = 0.0)¶
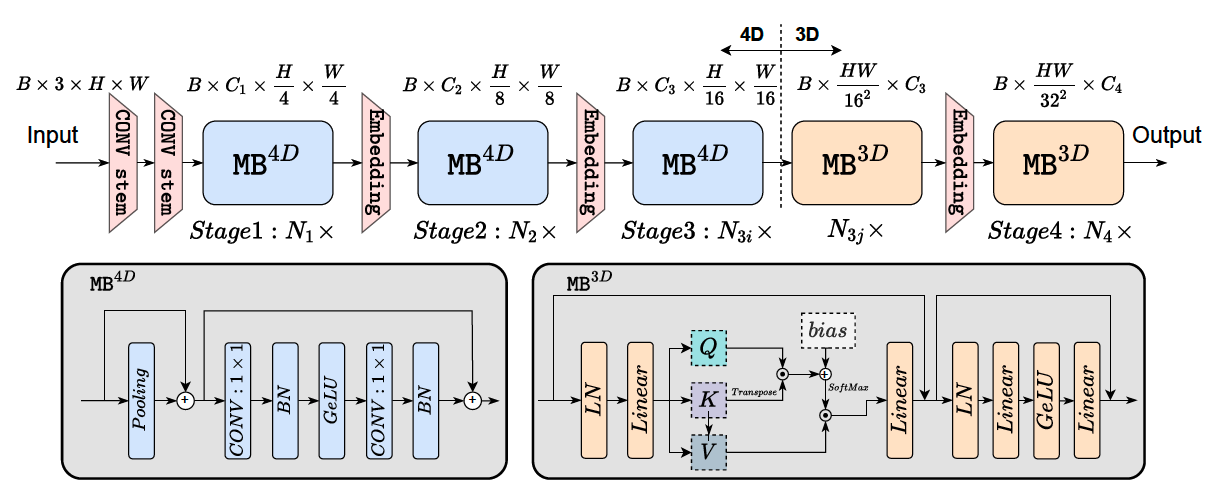
The EfficientFormer module implements a lightweight hybrid vision transformer architecture optimized for mobile and edge devices. It combines convolutional and transformer-based components in a streamlined hierarchical design to achieve high efficiency and competitive accuracy.
Class Signature¶
class EfficientFormer(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
depths: list[int],
embed_dims: int | None = None,
in_channels: int = 3,
num_classes: int = 1000,
global_pool: bool = True,
downsamples: list[bool] | None = None,
num_vit: int = 0,
mlp_ratios: float = 4.0,
pool_size: int = 3,
layer_scale_init_value: float = 1e-5,
act_layer: type[nn.Module] = nn.GELU,
norm_layer: type[nn.Module] = nn.BatchNorm2d,
norm_layer_cl: type[nn.Module] = nn.LayerNorm,
drop_rate: float = 0.0,
proj_drop_rate: float = 0.0,
drop_path_rate: float = 0.0,
) -> None
Parameters¶
depths (list[int]): Depth of each stage in the EfficientFormer hierarchy.
embed_dims (int | None, optional): Base embedding dimension. If None, it is derived from model size. Default is None.
in_channels (int, optional): Number of input image channels. Default is 3.
num_classes (int, optional): Number of classes for the classification head. Default is 1000.
global_pool (bool, optional): Whether to apply global average pooling before the classifier. Default is True.
downsamples (list[bool] | None, optional): Whether to downsample at each stage. If None, defaults to standard configuration.
num_vit (int, optional): Number of stages using transformer blocks. Remaining stages use convolutions. Default is 0.
mlp_ratios (float, optional): MLP expansion ratio in transformer blocks. Default is 4.0.
pool_size (int, optional): Kernel size for the pooling layer in convolution stages. Default is 3.
layer_scale_init_value (float, optional): Initial value for layer scale in transformer stages. Default is 1e-5.
act_layer (type[nn.Module], optional): Activation function used throughout the model. Default is nn.GELU.
norm_layer (type[nn.Module], optional): Normalization layer used in convolution stages. Default is nn.BatchNorm2d.
norm_layer_cl (type[nn.Module], optional): Normalization layer used in classification layers. Default is nn.LayerNorm.
drop_rate (float, optional): Dropout rate for embedding dropout. Default is 0.0.
proj_drop_rate (float, optional): Dropout rate for projection layers. Default is 0.0.
drop_path_rate (float, optional): Drop path rate for stochastic depth. Default is 0.0.
Architecture¶
EfficientFormer combines the strengths of convolutional inductive bias and transformer flexibility in a stage-wise hybrid design:
Convolutional Stages:
Early stages use lightweight depthwise-separable convolutions.
Convolution + BatchNorm + Activation (CBR) blocks dominate these layers.
Transformer Stages:
Later stages use efficient self-attention with MLPs and normalization.
Employs simplified attention to reduce complexity while maintaining accuracy.
MetaBlock:
The MetaBlock is the core computational unit used in both convolutional and transformer stages.
In convolutional mode, MetaBlock uses depthwise separable convolutions with residual connections.
In transformer mode, it applies a simplified attention mechanism followed by a feed-forward MLP block.
It supports layer scaling, drop path, and residual connections, enabling stable and deep training.
MetaBlocks unify the design across different stages, reducing architectural complexity while retaining flexibility.
Hierarchical Design:
Embedding dimensions grow progressively through stages.
Optional downsampling after each stage.
Classification Head:
Global average pooling followed by a LayerNorm and linear classifier.
Examples¶
Basic Usage
import lucid
from lucid.models.transformer import EfficientFormer
# Create a default EfficientFormer model
model = EfficientFormer(depths=[2, 2, 6, 2], num_vit=2)
input_tensor = lucid.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
output = model(input_tensor)
print(output.shape) # Shape: (1, 1000)
Custom Configuration
model = EfficientFormer(
depths=[3, 3, 9, 3],
embed_dims=64,
num_vit=3,
num_classes=100,
drop_rate=0.1,
drop_path_rate=0.1
)
input_tensor = lucid.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
output = model(input_tensor)
print(output.shape) # Shape: (1, 100)
Tip
Increase the number of transformer stages (num_vit) to enhance long-range feature modeling.
Warning
The depths list must match the number of model stages, and num_vit should not exceed that length.