YOLO-v3¶
ConvNet One-Stage Detector Object Detection
- class lucid.models.YOLO_V3(num_classes: int, anchors: list[tuple[int, int]] | None = None, image_size: int = 416, darknet: Module | None = None, darknet_out_channels_arr: list[int] | None = None)¶
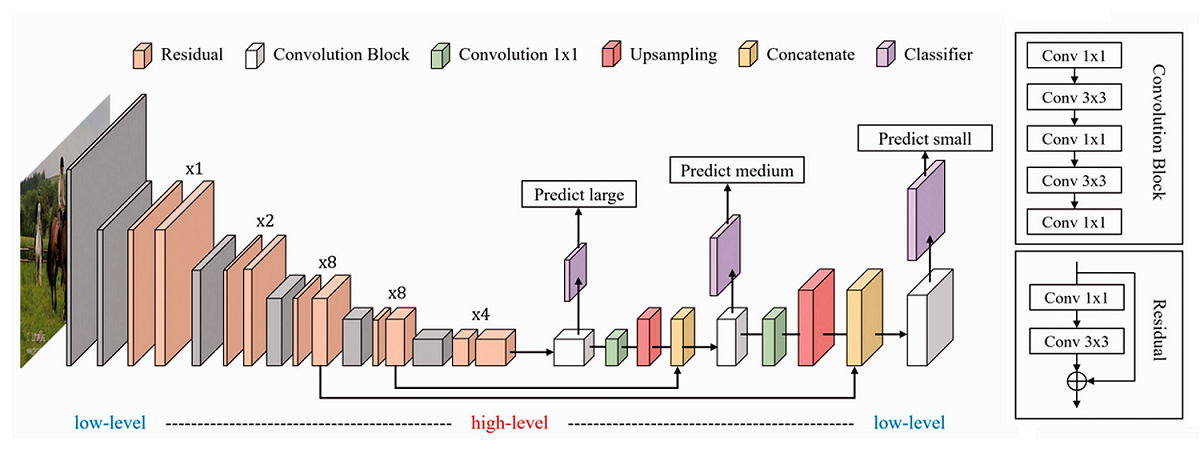
The YOLO_V3 class implements the YOLO-v3 object detection model, extending YOLO-v2 by using multi-scale feature maps, residual connections, and deeper backbones (Darknet-53).
Class Signature¶
class YOLO_V3(
num_classes: int,
anchors: list[tuple[float, float]] | None = None,
image_size: int = 416,
darknet: nn.Module | None = None,
)
Parameters¶
num_classes (int): Number of object classes for detection.
anchors (list[tuple[float, float]], optional): List of predefined anchor box sizes. If None, the model uses the default 9 YOLO-v3 anchors.
darknet (nn.Module, optional): Optional custom Darknet-53-style backbone. If not provided, the model uses the default one.
Important
To pre-train Darknet-53 as a classification task, set classification=True in the forward pass of YOLO_V3.darknet. This returns the classification logits rather than multi-scale feature maps for detection tasks.
image_size (int): Size of the input image (default is 416).
Attributes¶
darknet (nn.Module): Feature extraction backbone, typically Darknet-53.
Methods¶
Multi-Scale Detection¶
YOLO-v3 performs detection at three different scales, targeting small, medium, and large objects by upsampling and concatenating intermediate features:
13x13 grid (stride=32): large objects
26x26 grid (stride=16): medium objects
52x52 grid (stride=8): small objects
Each detection head outputs 3 bounding boxes per grid cell, using specific anchor subsets.
Input Format¶
The target should be a tuple of 3 elements (one for each scale), each with shape:
(N, Hs, Ws, B * (5 + C))
Where:
Hs, Ws are the grid size of the scale (13, 26, or 52 for input 416),
B is the number of anchors (typically 3 per scale),
C is number of classes.
Each vector at \((i, j)\) of shape \((B * (5 + C))\) contains:
For each box \(b\): \((t_x, t_y, t_w, t_h, obj, cls_1, \cdots, cls_C)\)
Where:
\(t_x, t_y\): offset of box center within the cell (\(\in [0,1]\))
\(t_w, t_h\): log-scale of box size relative to anchor (log((gw/s)/aw)) (canonical YOLO-v3 form)
\(obj\): 1 if anchor is responsible for object, else 0
\(cls_{1\ldots }C\): one-hot class vector
YOLO-v3 Loss¶
YOLO-v3 uses an anchor-based multi-part loss across three scales. Each scale contributes to the final loss by computing coordinate, objectness, and class probabilities.
Where:
\(\hat{t}_{x,y,w,h}\) are raw outputs
\(t_{x,y}\) are cell-relative offsets
\(t_{w,h}\) are log-ratio targets (canonical encoding)
\(\hat{C}\) is objectness after sigmoid
\(\hat{p}(c)\) is predicted class prob after sigmoid
Prediction Output¶
The predict method applies decoding, confidence thresholding, and non-maximum suppression (NMS). It returns a list of detections per image, where each detection is a dictionary:
“box”: Tensor [x1, y1, x2, y2] in image pixels
“score”: objectness * class prob
“class_id”: predicted class index
Example Usage¶
Using YOLO-V3 with default anchors and backbone
>>> from lucid.models import YOLO_V3
>>> model = YOLO_V3(num_classes=80)
>>> x = lucid.random.rand(2, 3, 416, 416)
>>> preds = model.predict(x)
>>> print(preds[0][0])
Backward Propagation¶
The YOLO-V3 model supports gradient backpropagation through all layers:
>>> x = lucid.random.rand(1, 3, 416, 416, requires_grad=True)
>>> targets = (...) # 3-scale tuple of target tensors
>>> loss = model.get_loss(x, targets)
>>> loss.backward()
>>> print(x.grad)