VAE¶
Autoencoder Variational Autoencoder Image Generation
- class lucid.models.imggen.VAE(encoders: list[Module], decoders: list[Module], priors: list[Module] | None, reconstruction_loss: Literal['mse', 'bce'] = 'mse', kl_weight: float = 1.0, beta_schedule: Callable[[int], float] | None = None, hierarchical_kl: bool = True, depth: int | None = None)¶
The VAE class implements a generalized Variational Autoencoder supporting standard and hierarchical variants. It is compatible with various encoder-decoder architectures and prior configurations.
This model is modular, allowing users to define multiple layers of latent variables and optionally plug in learnable prior modules for deep hierarchies. It is designed to support \(\beta\)-scheduling and flexible loss configurations.
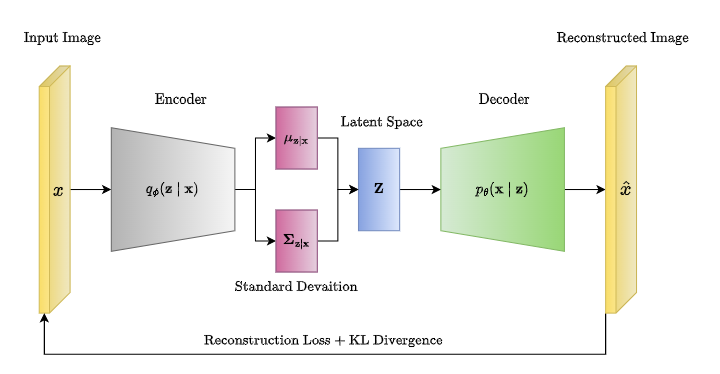
Class Signature¶
class VAE(
encoders: list[nn.Module],
decoders: list[nn.Module],
priors: list[nn.Module] | None = None,
reconstruction_loss: Literal["mse", "bce"] = "mse",
kl_weight: float = 1.0,
beta_schedule: Callable[[int], float] | None = None,
hierarchical_kl: bool = True,
depth: int | None = None,
)
Parameters¶
encoders (list[nn.Module]): A list of encoder modules. Each encoder should output a tensor of shape (N, 2 * D) where the first half encodes the mean and the second half the log-variance of the Gaussian latent variable.
decoders (list[nn.Module]): A list of decoder modules. Decoding starts from the deepest latent and reconstructs to the original data space.
priors (list[nn.Module] | None): Optional list of prior modules that map the latent from the next layer into a prior distribution (output shape must be (N, 2 * D)).
reconstruction_loss (Literal[“mse”, “bce”]): Type of reconstruction loss to apply. Either Mean Squared Error (MSE) or Binary Cross Entropy (BCE).
kl_weight (float): The default \(\beta\) weighting applied to KL divergence.
beta_schedule (Callable[[int], float] | None): Optional function that outputs \(\beta\) for each training step.
hierarchical_kl (bool): If True, distributes KL loss over all latent layers; otherwise applies \(\beta\) to each layer equally.
depth (int | None): Optionally set the number of latent layers manually. If not provided, it defaults to the number of encoders.
Returns¶
Use the forward method to obtain outputs:
recon, mus, logvars, zs = model(x)
recon (Tensor): Reconstructed tensor in original input shape.
mus (list[Tensor]): Means for each latent layer.
logvars (list[Tensor]): Log-variances for each latent layer.
zs (list[Tensor]): Sampled latent vectors after reparameterization.
Loss Components¶
Use the method get_loss() to compute total VAE loss:
loss, recon_loss, kl = model.get_loss(x, recon, mus, logvars, zs)
Where:
recon_loss: is the MSE or BCE loss.
kl: total KL divergence (may be hierarchical).
loss: full objective: \(\mathcal{L} = \text{recon} + \beta \cdot \text{KL}\)
Methods¶
- VAE.current_beta() float¶
Module Output Requirements¶
The encoder modules in encoders list must return a Tensor of shape (N, 2 * D), which will be split into:
Similarly, priors modules (if provided) should accept a latent tensor from the deeper layer and output the same (N, 2 * D) format to define hierarchical priors.
Decoder modules in decoders list must accept a Tensor z and sequentially transform it back to the original input shape.
Examples¶
import lucid
import lucid.nn as nn
import lucid.nn.functional as F
from lucid.models.imggen import VAE
encoder = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(784, 512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(512, 128),
)
decoder = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(64, 512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(512, 784),
)
vae = VAE(
encoders=[encoder],
decoders=[decoder],
input_shape=(784,),
)
x = lucid.randn(32, 784)
recon, mus, logvars, zs = vae(x)
loss, recon_loss, kl = vae.get_loss(x, recon, mus, logvars, zs)
Note
This VAE class encompasses the standard VAE, \(\beta\)-VAE, and Hierarchical VAE (HAVE).
Tip
The reparameterization is implemented as:
Warning
Make sure the final decoder output is in the same shape and scale as the input, especially when using BCE loss, which expects values in \([0, 1]\).