Faster R-CNN¶
ConvNet Two-Stage Detector Object Detection
- class lucid.models.FasterRCNN(backbone: Module, feat_channels: int, num_classes: int, *, use_fpn: bool = False, anchor_sizes: tuple[int, ...] = (128, 256, 512), aspect_ratios: tuple[float, ...] = (0.5, 1.0, 2.0), anchor_stride: int = 16, pool_size: tuple[int, int] = (7, 7), hidden_dim: int = 4096, dropout: float = 0.5)¶
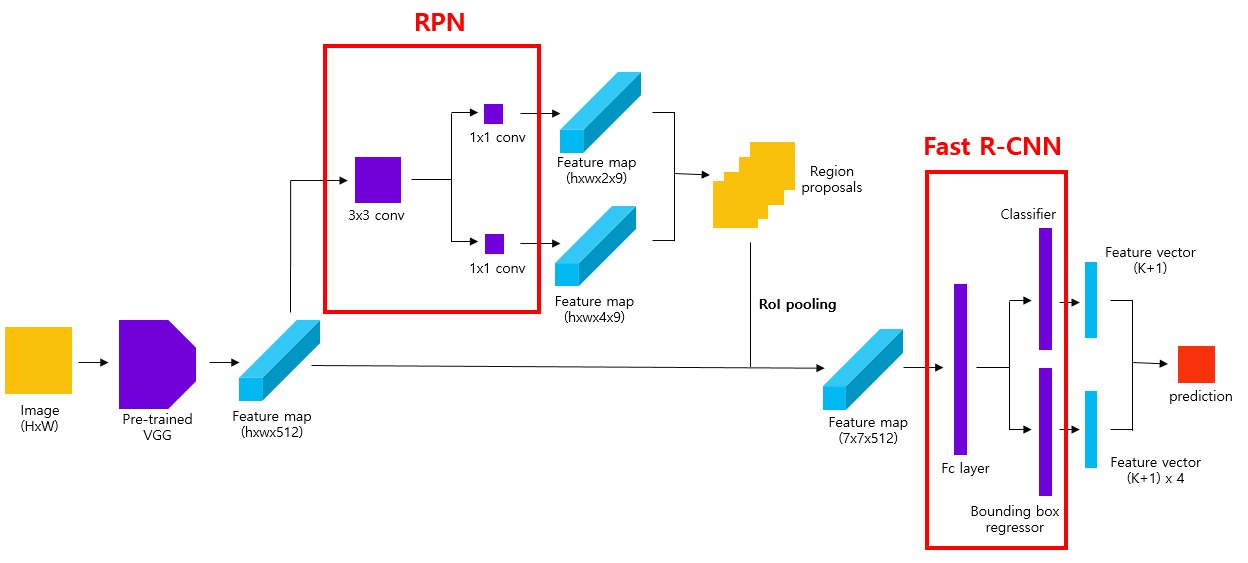
FasterRCNN implements the Faster Region-based Convolutional Neural Network, an improvement over Fast R-CNN that introduces a learnable Region Proposal Network (RPN). This architecture eliminates the need for external proposal methods by jointly learning region proposals and object classification in a unified network.
Class Signature¶
class FasterRCNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
backbone: nn.Module,
feat_channels: int,
num_classes: int,
*,
use_fpn: bool = False,
anchor_sizes: tuple[int, ...] = (128, 256, 512),
aspect_ratios: tuple[float, ...] = (0.5, 1.0, 2.0),
anchor_stride: int = 16,
pool_size: tuple[int, int] = (7, 7),
hidden_dim: int = 4096,
dropout: float = 0.5,
)
Parameters¶
backbone (nn.Module): Feature extraction network applied once per image to produce a feature map.
feat_channels (int): Number of output channels from the backbone’s final feature map.
num_classes (int): Number of object categories (excluding background).
use_fpn (bool, optional): Whether to use Feature Pyramid Network (FPN) for backbone feature extraction. Default is False. When set to True, the user should attach backbone model that supports FPN feature returns.
anchor_sizes (tuple[int, …], optional): Set of anchor box scales used by the RPN. Default is (128, 256, 512).
aspect_ratios (tuple[float, …], optional): Set of aspect ratios for the anchors. Default is (0.5, 1.0, 2.0).
anchor_stride (int, optional): Stride of the anchor generation relative to the backbone feature map. Default is 16.
pool_size (tuple[int, int], optional): Spatial size of each RoI feature after pooling. Default is (7, 7).
hidden_dim (int, optional): Number of units in the fully connected head. Default is 4096.
dropout (float, optional): Dropout probability used in the classification and regression head. Default is 0.5.
Architecture¶
Faster R-CNN enhances Fast R-CNN by replacing external proposal mechanisms with a learnable RPN:
Feature Map Extraction:
The image is processed by the backbone to produce a dense feature map.
Region Proposal Network (RPN):
Anchors are placed over the feature map.
The RPN classifies whether each anchor contains an object and regresses its bounding box.
RoI Pooling:
High-confidence proposals are selected and pooled to a fixed size (pool_size).
Detection Head:
Each RoI is processed by fully connected layers for classification and bounding box refinement.
Loss Output:
The model provides a .get_loss() method, returning a structured loss dictionary.
Loss Dictionary¶
class _FasterRCNNLoss(TypedDict):
rpn_cls_loss: Tensor
rpn_reg_loss: Tensor
roi_cls_loss: Tensor
roi_reg_loss: Tensor
total_loss: Tensor
Returned by FasterRCNN.get_loss(), this dictionary provides detailed loss breakdowns for both RPN and RoI heads.
Examples¶
Basic Usage
import lucid.nn as nn
import lucid.random
class SimpleBackbone(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.ReLU()
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.conv(x)
backbone = SimpleBackbone()
model = nn.FasterRCNN(backbone, feat_channels=128, num_classes=5)
image = lucid.random.randn(1, 3, 512, 512)
output = model.predict(image)
print(output["boxes"].shape, output["scores"].shape, output["labels"].shape)
Custom Configuration
backbone = SimpleBackbone()
model = nn.FasterRCNN(
backbone=backbone,
feat_channels=128,
num_classes=5,
anchor_sizes=(64, 128, 256),
aspect_ratios=(0.5, 1.0),
pool_size=(5, 5),
hidden_dim=2048,
dropout=0.4,
)
image = lucid.random.randn(1, 3, 384, 384)
output = model.predict(image)
print(output["boxes"].shape, output["scores"].shape, output["labels"].shape)
Tip
For training, use model.get_loss() with the predicted and ground-truth targets to compute total and component-wise loss terms.