Fast R-CNN¶
ConvNet Two-Stage Detector Object Detection
- class lucid.models.FastRCNN(backbone: Module, feat_channels: int, num_classes: int, pool_size: tuple[int, int] = (7, 7), hidden_dim: int = 4096, bbox_reg_means: tuple[float, ...] = (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0), bbox_reg_stds: tuple[float, ...] = (0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2), dropout: float = 0.5, proposal_generator: Callable[[...], Tensor] | None = None)¶
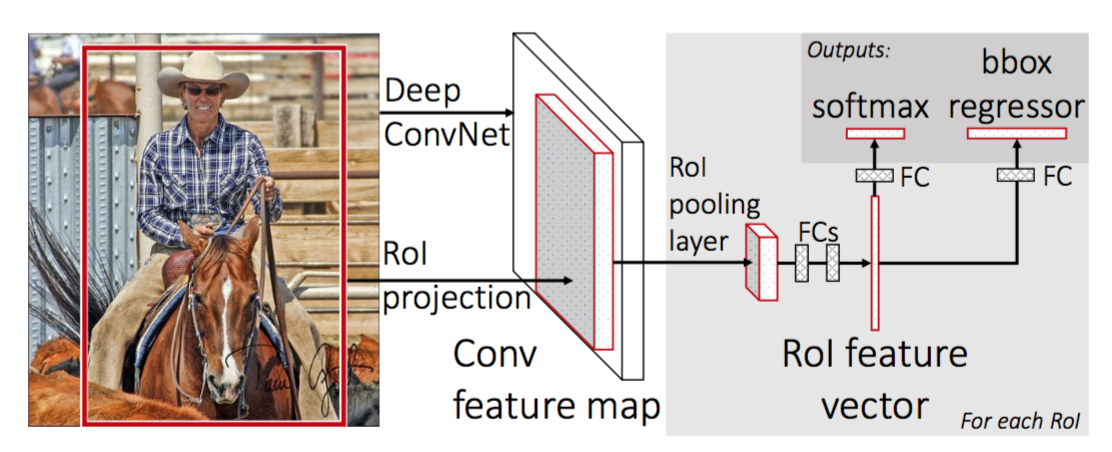
FastRCNN implements the Fast Region-based Convolutional Neural Network architecture for object detection, building upon the R-CNN approach by introducing a more efficient detection pipeline. It replaces per-region feature extraction with RoI pooling and integrates classification and bounding box regression into a single forward pass.
Class Signature¶
class FastRCNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
backbone: nn.Module,
feat_channels: int,
num_classes: int,
pool_size: tuple[int, int] = (7, 7),
hidden_dim: int = 4096,
bbox_reg_means: tuple[float, ...] = (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0),
bbox_reg_stds: tuple[float, ...] = (0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2),
dropout: float = 0.5,
proposal_generator: Callable[..., Tensor] | None = None,
)
Parameters¶
backbone (nn.Module): Convolutional feature extractor applied over the entire image once.
feat_channels (int): Number of output channels from the backbone feature map.
num_classes (int): Number of object categories (excluding background).
pool_size (tuple[int, int], optional): Output size of the spatial pooling operation (typically RoIAlign or RoIPool). Default is (7, 7).
hidden_dim (int, optional): Number of hidden units in the fully connected layers after pooling. Default is 4096.
bbox_reg_means (tuple[float, …], optional): Normalization means for bounding box regression targets. Default is (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0).
bbox_reg_stds (tuple[float, …], optional): Normalization stds for bounding box regression targets. Default is (0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2).
dropout (float, optional): Dropout probability used in the fully connected layers. Default is 0.5.
proposal_generator (Callable[…, Tensor] | None, optional): Custom region proposal function. If None, uses precomputed proposals.
Architecture¶
Fast R-CNN improves over the original R-CNN by computing the CNN feature map once per image and classifying object proposals directly on this shared map:
Full-Image Feature Map:
The input image is passed through the backbone to extract a dense feature map.
Region of Interest (RoI) Pooling:
Region proposals are projected onto the feature map and cropped to a fixed size using RoI pooling (size defined by pool_size).
Two-Stream Head:
Each pooled region is passed through a set of fully connected layers.
One stream performs classification over num_classes.
The other stream regresses bounding box adjustments per class.
Bounding Box Normalization:
Regression outputs are scaled using bbox_reg_means and bbox_reg_stds.
Examples¶
Basic Usage
import lucid.nn as nn
import lucid.random
import lucid
class ToyBackbone(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.ReLU()
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.net(x)
# Instantiate model
backbone = ToyBackbone()
model = nn.FastRCNN(backbone, feat_channels=64, num_classes=4)
# Dummy input
image = lucid.random.randn(1, 3, 512, 512)
output = model.predict(image)
print(output["boxes"].shape, output["scores"].shape, output["labels"].shape)
Explanation
Fast R-CNN accelerates inference by removing redundant computation. A single backbone pass generates features, which are then reused for each region proposal. RoI pooling ensures a fixed-size input for classification and regression heads.
Custom Configuration
class MiniBackbone(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.ReLU()
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.conv(x)
backbone = MiniBackbone()
model = nn.FastRCNN(
backbone=backbone,
feat_channels=32,
num_classes=3,
pool_size=(5, 5),
hidden_dim=1024,
dropout=0.3,
)
image = lucid.random.randn(1, 3, 256, 256)
output = model.predict(image)
print(output["boxes"].shape, output["scores"].shape, output["labels"].shape)